Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The list of supported guest operating systems may always be extended.
Please check the official Microsoft Hyper-V site to obtain a current list of
Hyper-V Architecture
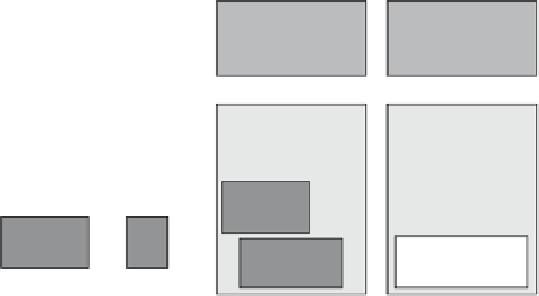
This section will provide you with an overview of the Hyper-V architecture (see Figure 9.1).
I'll explain the differences between a hypervisor-aware and a non-hypervisor-aware child
partition.
figUre 9.1
Hyper-V architecture
Parent partition
Child partitions
Virtualization stack
WMI provider
Applications
Applications
Applications
VM worker
process
VM service
User mode
Windows Server
2008
Hypervisor-aware
OS (e.g., Windows
Server 2003, 2008)
Xen-enabled Linux
kernel
Non-hypervisor-
aware OS
Windows
kernel
Windows
kernel
VSP
Integration
components
Linux Integration
components
Kernel mode
Emulation
VMBus
Hyper-V hypervisor
Hardware
As you can see, Hyper-V is based on the new microkernel architecture. Hyper-V
provides a virtualization layer called a
hypervisor
that runs directly on the system
hardware. You can see that the hypervisor is similar to what the kernel is to Windows.
It is a software layer responsible for the interaction with the core hardware and works in
conjunction with an optimized instance of Windows Server 2012 R2 that allows running
multiple operating systems on a physical server simultaneously. The Hyper-V architecture
consists of the hypervisor and parent and child partitions.
The Windows Server 2012 R2 operating system runs in the parent partition, and it
delivers the WMI provider for scripting as well as the VM service.





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search