Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
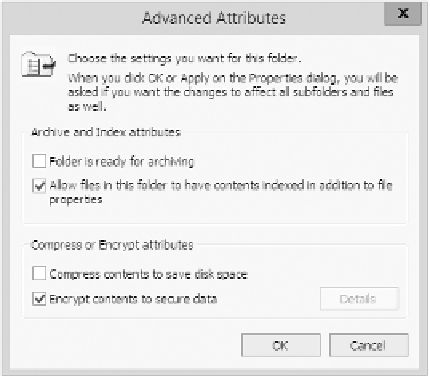
(SID) number to secure the file or folder. To implement encryption, open the Advanced
Attributes dialog box for a folder and check the Encrypt Contents To Secure Data box
(see Figure 4.3).
figuRe 4.3
Setting up encryption on a folder
If files are encrypted using EFS and an administrator has to unencrypt the files, there
are two ways to do this. First, you can log in using the user's account (the account that
encrypted the files) and unencrypt the files. Second, you can become a recovery agent and
manually unencrypt the files.
If you use EFS, it's best not to delete users immediately when they
leave a company. Administrators have the ability to recover encrypted
files, but it is much easier to gain access to the user's encrypted files by
logging in as the user who left the company and unchecking the encryp-
tion box.
Security
One of the biggest advantages of NTFS is security. Security is one of the
most important aspects of an IT administrator's job. An advantage of NTFS security is that
the security can be placed on individual files and folders. It does not matter whether you
are local to the share (in front of the machine where the data is stored) or remote to
the share (coming across the network to access the data); the security is always in place
with NTFS.
The default security permission is
Users = Read
on new folders or shares.
NTFS security is
additive
. In other words, if you are a member of three groups
(Marketing, Sales, and R&D) and these three groups have different security settings,
you get the highest level of permissions. For example, let's say you have a user by
the name of wpanek who belongs to all three groups (Marketing, Sales, and R&D).



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search