Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
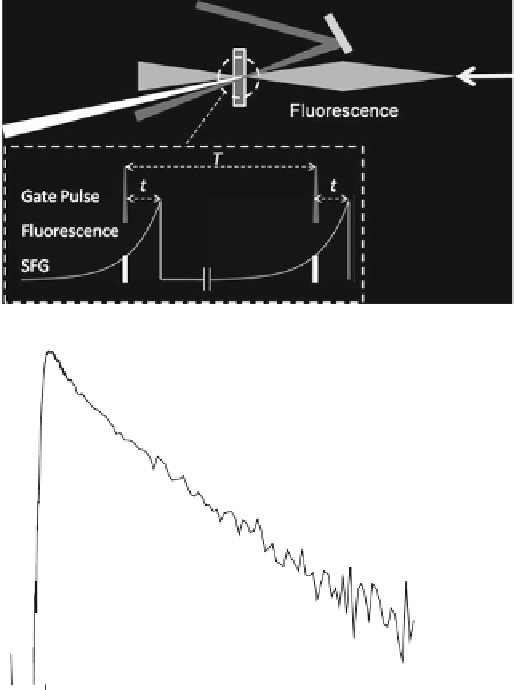
Since the SFG is generated by one fluorescence photon and one pulse photon, it can
only be generated when both are present, and its intensity thus reflects the instanta-
neous intensity of the fluorescence (Fig.
2a
) during the 800 nm pulse. Essentially the
SFG samples the fluorescence intensity at the arrival time of the 800 nm pulse. By
scanning the time delay between pump and probe, the SFG intensity maps out the
fluorescence decay (Fig.
2b
).
The SFG signal is detected in the UV region by a low noise photon counting
photomultipler placed behind a monochromator, which selects the fluorescence
wavelength (which is also optimised by angle tuning the SFG crystal). The time
resolution is recorded by up-converting the instantaneous Raman radiation scattered
a
b
1
0.1
0.01
1E-3
0
2
4
Delay Time / ps
Fig. 2 (a) Schematic of the SFG process used for time resolution in up-conversion. (b)An
example of an ultrafast fluorescence decay profile (anionic HBDI in ethanol) plotted on a log
scale (excitation was at 400 nm with a sub 50 fs pulse and emission was detected at the peak of the
fluorescence)

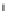











Search WWH ::

Custom Search