Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 7.10
ANOVA for selected variables related to
Phailin
Variables
of debris created a logistical nightmare for sur-
vivors and those trying to assist them.
F
F
obs
crit
Salinity
Between phases
7.2
Anthropogenic Threats
85.53508
3.837853
Between stations
1,531.787
4.45897
Anthropogenic factors are human activities that
change the environment and in
p
Between phases
uence climate.
The emission of carbon dioxide due to burning of
fossil fuels or the increase of greenhouse gas
concentrations due to rapid urbanization, indus-
trialization and expansion of unplanned tourism
are unquestionable human in
fl
1,017
3.837853
Between stations
4.333333
4.45897
DO
Between phases
38.70268
3.837853
Between stations
10.83638
4.45897
uences on coastal
vegetation through the event of habitat destruc-
tion or modi
fl
Chlorophyll a
Between phases
13.80891
3.837853
cation. However, in some cases, the
chain of causality is direct and unambiguous (e.g.
the effects clearance of the coastal vegetation for
setting industries or shrimp farms), while in
others, it is less clear (e.g. the effect of acidi
Between stations
38.45118
4.45897
Phytoplankton
Between phases
8.521948
3.837853
Between stations
84.37756
4.45897
-
cation on coastal vegetation in terms of bioac-
cumulation and mortality).
Today, the climate change-related researches
unanimously suggest that the biggest factor of
alteration of blue carbon reservoir is the increase
in carbon dioxide levels due to emissions from
fossil fuel combustion, followed by aerosols
(particulate matter in the atmosphere), which
exert a cooling effect. Other factors, including
change of land use, animal grazing, agriculture
ever recorded. It was accompanied by a storm
surge that smashed through coastal neighbour-
hoods and farmlands across much of the central
Philippines (Fig.
7.31
). Preparations and early
warnings saved many lives. Despite of this pre-
paredness, thousands died and millions were left
in need of urgent assistance. Local of
cials and
emergency response teams were themselves ini-
tially shaken, as swamps of sea water and jungles
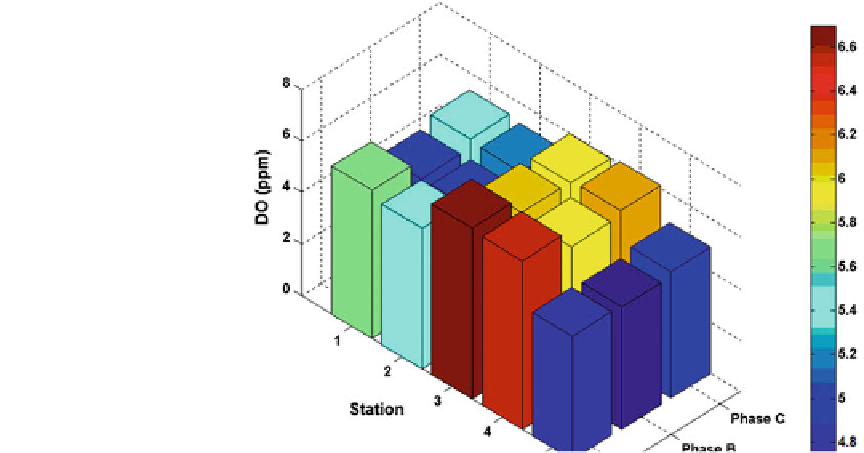
Fig. 7.28
Variation of DO
during pre-Phailin (Phase
A), Phailin (Phase B) and
post-Phailin (
Phase C
)
periods