Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
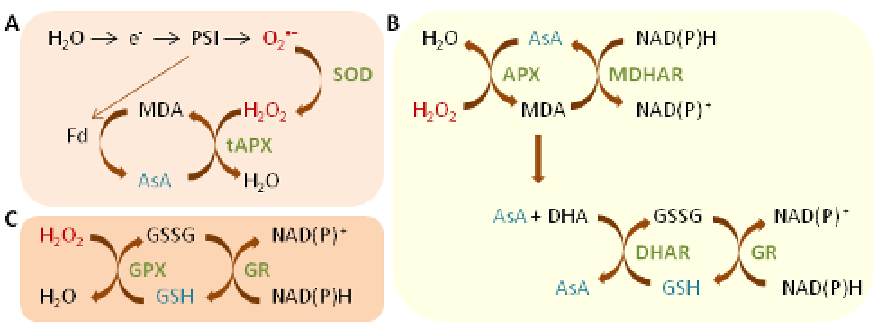
Figure 4.
Different pathways for ROS scavenging in plants: A - the water-water cycle (Mehler reaction); B - the ascor‐
bate-glutathione cycle; C - the glutathione peroxidase cycle. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) acts as the first line of de‐
fense converting O
2
•−
into H
2
O
2
, then ascorbate peroxidases (APX), glutathione peroxidases (GPX) and catalases (CAT -
not shown) eliminate H
2
O
2
. In contrast to CAT, both APX and GPX require ascorbate (AsA) or glutathione (GSH) regen‐
erating cycles that use electrons from the photosynthesis (A) or NAD(P)H (B, C) as reducing power. ROS are indicated
in red, ROS-scavenging enzymes in green and low-molecular antioxidants in blue. Abbreviations: DHA - dehydroascor‐
bate; DHAR - DHA reductase; Fd - ferredoxin; GR - glutathione reductase; GSSG - oxidized glutathione; MDA - mono‐
dehydroascorbate; MDAR - MDA reductase; PSI - photosystem I; tAPX - thylakoid-bound APX (according to Mittler et
al., 2004) [73].
Catalases are tetrameric enzymes containing heme with the potential to dismutate H
2
O
2
into
H
2
O and O
2
.
2H
2
O
2
→ 2H
2
O + O
2
CAT1 and CAT2 are localized in peroxisomes and cytosol, whereas CAT3 is targeted to mi‐
tochondria. Increased CAT activity has been reported in various abiotic stress studies in dif‐
ferent species, e.g. under drought stress in wheat [103]. Moreover, a vast number of research
indicate that CAT overexpression leads to the abiotic stress tolerance, e.g. wheat catalase ex‐
pressed in transgenic rice has been demonstrated to improve the tolerance against low tem‐
peratures [104].
Another group of antioxidising enzymes - ascorbate peroxidases are involved in H
2
O
2
scav‐
enging in water-water and glutathione-ascorbate cycles and use ascorbic acid as the electron
donor (Figure 4A and B). The reaction catalysed by APXs is the transfer of electrons from
ascorbate to hydrogen peroxide, producing dehydroascorbate and water
H
2
O
2
+ C
6
H
8
O
6
→ 2H
2
O + C
6
H
6
O
6
In
Arabidopsis thaliana
, the presence of eight APX isoenzymes has been confirmed: soluble
cytosolic (APX1, APX2, APX6), bounded to the microsome membrane (APX3, APX4, APX5),
chloroplast stromal (sAPX) and thylakoid (tAPX). Higher expression levels of APXs have
been demonstrated during different stress conditions and their overexpression has been pro‐
Search WWH ::

Custom Search