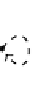Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
This can be done by following the strategy illustrated in Fig. 1.
5
We shall explain
this in detail in the following. Let
p
:= (
p
1
,...,p
m
) be a sequence listing natural
{
1
,...,n
}
p
), we first show how to choose
M
and
N
,for
numbers of
.Formid(
each 0
≤
i
≤
m
,sothat
ʵ
(
c
)
c
ʵ
(
x
1
)
x
1
N
ʵ
(
ʲ
)
ʲ
ʱ
x
3
M
x
2
b
n
Spoiler
Duplicator
1
−k
k
Fig. 1
5
AplayofEF
m
((
A
,
b
,
c
)
,
(
A
,
b
,ʵ
(
c
)) where Spoiler picks members of (
A
,
b
,
c
)andDu-
plicator picks members of (
A
,
b
,ʵ
(
c
)) according to her winning strategy is illustrated
in Fig. 1. The idea is that after each round
i ≤ m
,
M
and
N
are placed so that
N − M ≥
2
m
+1
−i
.Alsoforeach
j ≤ i
,
y
j
=
x
j
if row(
x
j
)
≤ M
,and
y
j
=
ʵ
(
x
j
)if
row(
x
j
)
≥ N
,where
y
j
and
x
j
represent Duplicator's and Spoiler's choices, respec-
tively. In the picture,
ʱ
and
ʲ
represent two alternative choices Spoiler can make
at the fourth round. If Spoiler chooses
x
4
:=
ʱ
, then Duplicator chooses
y
4
:=
ʱ
,
and
M
is moved to row(
ʱ
). If Spoiler chooses
x
4
:=
ʲ
, then Duplicator chooses
y
4
:=
ʵ
(
ʲ
), and
N
is moved to row(
ʲ
). Proceeding in this way we obtain that at
the final stage
m
,(
A
,
b
,
c
,x
1
,...,x
m
)and(
A
,
b
,ʵ
(
c
)
,y
1
,...,y
m
) agree on all atomic
FO[
˄
]formulae.