Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
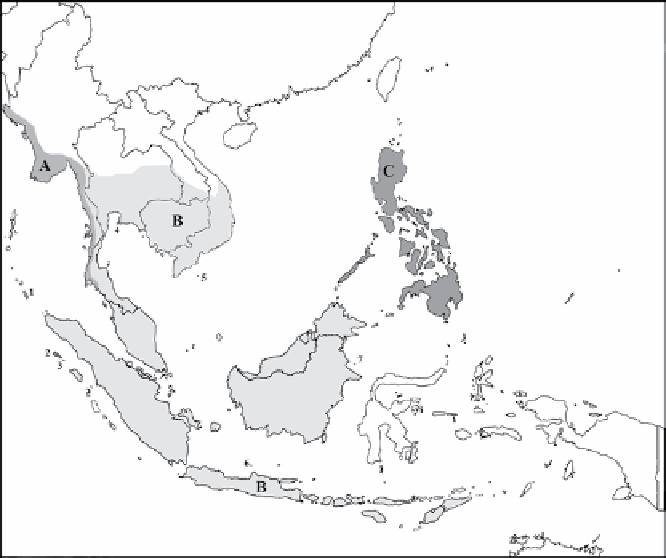
Figure 1.2. A map of the distribution of the ten sub-species of
M. fascicularis
. The
core and its fringing subspecies are shaded and labeled by letters. A =
M. f. aurea
,
B =
M. f. fascicularis
, C =
M. f. philippinensis
. The isolated island subspecies are
labeled with numbers. 1 =
M. f. umbrosa
, 2 =
M. f. lasiae
, 3 =
M. f. fusca
,
4 =
M. f. atriceps
, 5 =
M. f. condorensis
, 6 =
M. f. karimondjiwae
, 7 =
M. f. tua
.
of mainland Southeast Asia east of Thailand, and extends through the major
islands of Indonesia and slightly extends into the southwestern region of the
Philippines (
Figure 1.2
).
Two other subspecies lie on the eastern and western extremes of the core
species' geographical distribution. The second largest ranging subspecies,
M. f. aurea
, is found northwest of the range of
M. f. fascicularis
in Myanmar,
Bangladesh, and west-central Thailand. They have a contact zone with
M. f. fas-
cicularis
along the mountain ranges that cover the border regions of Myanmar
and Thailand.
M. f. philippinensis
occupies a similarly sized range on the east-
ern side, occupying the majority of the Philippine islands except for the western
region of Mindanao, which is solely occupied by
M. f. fascicularis
. The ranges
of
M. f. fascicularis
and
M. f. philippinensis
overlap in the eastern two-thirds of
Mindanao and in the southern Negros Islands. Here the two subspecies are sym-
patric and long-tailed macaques of mixed phenotype can be found.