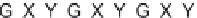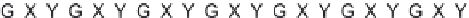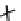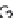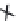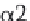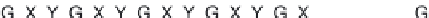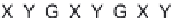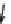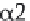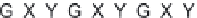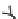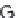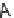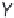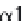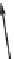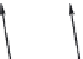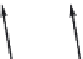what-when-how
In Depth Tutorials and Information
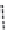
(A)
(B)
(C)
FIGURE 11.3
Possible long-term propagation of local conformational changes: (A) normal triple helix; (B) single-chain Gly→Cys mutation
causes looping out of the mutated chain, and leads to loss of GXY registration of interaction triplets with triplets on other two chains;
14
(C) all
three chains with Gly→Ala mutation result in loss of phase in triple-helix orientation and loss of direct hydrogen bonding.
11
the collagen triple helix. Part of the difficulty stems
from the dominant nature of OI missense mutations,
which leads to a heterogeneous mixture of molecular
species. A mutation in the α1(I) chain will lead to 25%
normal trimers, 50% molecules containing one mutant
α1(I) chain and 25% molecules with two mutant α1(I)
chains; while a mutation in the α2(I) chain will lead to
50% normal molecules and 50% molecules containing
a mutant α2(I) chain. One defined molecular species
cannot be isolated from this mixture, with the excep-
tion of disulfide bonded trimers when there are two
chains with Gly→Cys mutations. Rotary shadowing
has shown that several OI collagens with Gly→Cys
α1(I) mutations have a small percentage of molecules
with kinks located near the mutation site,
14,16,17
and it
was suggested such kinks may reflect small amounts
of trimers with disulfide bonds. However, a similar
kink was also reported for a Gly→Asp mutation in an
α2(I) chain,
18
so the kinking is not exclusive to Gly→Cys
mutations. A looping out of one or two chains at the
mutation site (
Figure 11.3B
) could generate a kink such
as that observed by Vogel et al.
14
Some mutations near the center of the triple helix
were shown to interfere with N-propeptide processing,
suggesting conformational consequences of a muta-
tion may be transmitted at a distance.
14,16,17
Type I col-
lagen folding is initiated at the C-terminus, and looping
out of one chain at the Gly missense mutation would
put the chains out of register in terms of their original
Gly-X-Y partners N-terminal to the defect, as well as
causing a kink (
Figure 11.3B
).
14
However, not all Gly
missense mutations lead to an N-propeptide processing