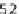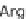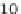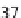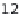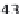what-when-how
In Depth Tutorials and Information
COL1A1
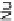
COL1A2
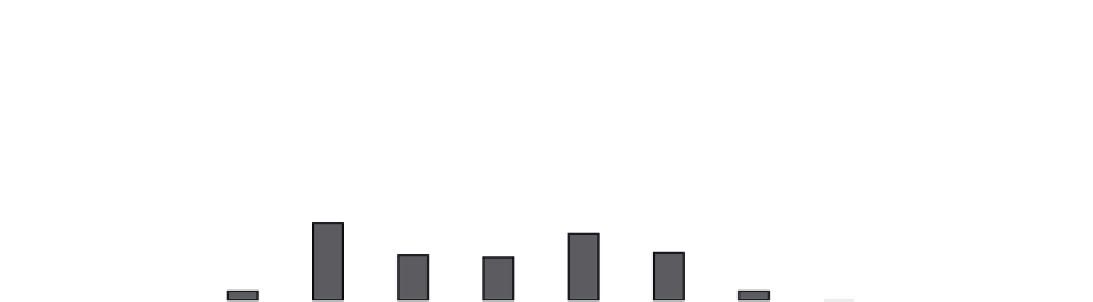
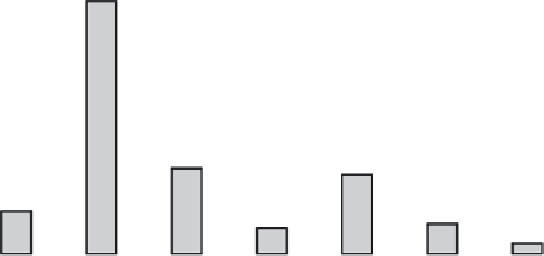
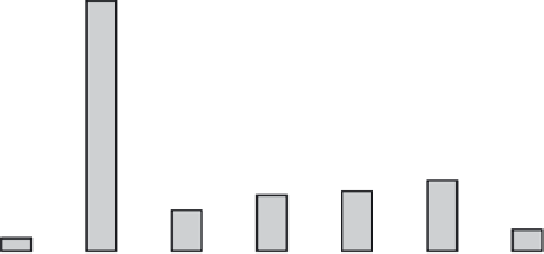
FIGURE 11.1
The frequency of Gly missense mutations observed in
COL1A1
and
COL1A2
genes, showing the number of lethal and non-
lethal for the eight possible missense mutations. (
Data taken from http://www.le.ac.uk/ge/collagen/
)
was the compilation of OI mutations determined by
many different research groups to provide a large data-
base which could be probed for clinical/structural cor-
relations.
2,3
Analysis of the database in terms of clinical
severity of mutations, location and local stability was
reported by Marini et al.,
2
with a thorough summary of
potential correlations and considerations. The current
Database of Osteogenesis Imperfecta Variants (
www.
le.ac.uk/ge/collagen/
updated 30 May 2012) now con-
tains 1685 variants observed in protein coding regions
of
COL1A1
and
COL1A2
genes (1065 and 620, respec-
tively).
3,4
The majority are missense mutations in the
triple-helix domain, of which ~94% represent replace-
ments of a Gly, while 6% occur in X- and Y-positions.
The Gly substitutions in the triple-helix domains of the
α1(I) chain (642 mutations) and α2(I) chain (524 muta-
tions) almost all lead to OI phenotypes, but the clinical
severity is highly variable, from mild to perinatal lethal
(
Figure 11.1
). About 36% of Gly missense mutations
(230/642) in the α1(I) chain result in the lethal type II
OI, while only 24% of the mutations in the α2(I) are
lethal (124/524). The small number of missense muta-
tions observed in the X- and Y-positions usually lead
to the milder non-OI phenotypes. One of the key ques-
tions which remains unanswered is why some Gly mis-
sense mutations are lethal, while nearby mutations are
mild or moderate.
A single base pair mutation in a Gly codon may result
in its replacement by one of eight amino acid residues:
Ala, Ser, Cys, Val, Arg, Asp, Glu and Trp. Although
mutation probabilities are different for these amino acid
substitutions, all of them were observed as missense
mutations in the
COL1A1
and
COL1A2
genes, including
a single occurrence of the rare Gly→Trp mutation (
Figure
11.1
). Gly→Ser are the most frequent mutations in both
α chains, but the ranking of imino acids differs in α1
and α2 chains. A strong correlation is observed between
the identity of the residue replacing Gly and the clinical
severity of the OI cases.
2,5
Gly→Ser and Gly→Cys muta-
tions may result in various outcomes when occurring at
different positions along the chain, while substitutions
to Val or charged residues (Arg, Glu, Asp) are almost
uniformly lethal when occurring at residue position
>200 in the α1(I) chain.
2
The mutation of the same Gly
may lead to different OI severity when substituted by
different amino acids. For example, at position Gly429
in the α1 chain, replacement by Ala leads to the mild-
est type I OI form, replacement by Cys leads to the OI
type IV (moderate form), and replacement by Asp leads
to a lethal type II OI case. The mutation spectrum for
Gly missense mutations observed in clinical databases
differs from that predicted on the basis of the indi-
vidual base pair mutation rates, suggesting that not all
of the Gly substitutions come to clinical attention.
5
For