Socket defines several instance methods. For example, a Socket can be examined at any
time for the address and port information associated with it, by use of the following methods:
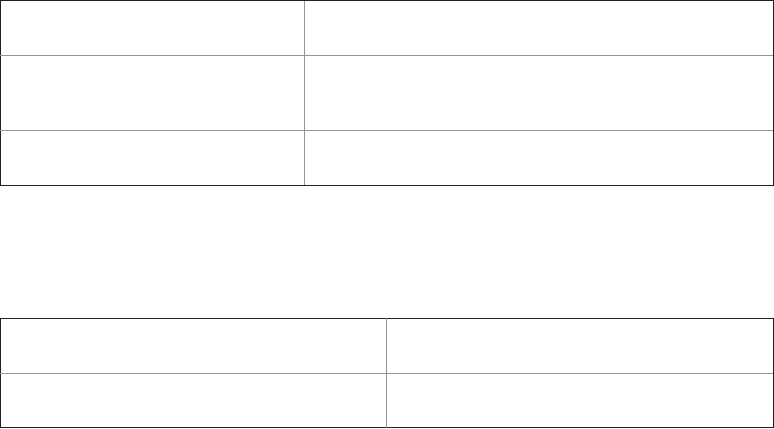
InetAddress getInetAddress( )
Returns the InetAddress associated with the Socket
object. It returns null if the socket is not connected.
int getPor t( )
Returns the remote por t to which the invoking Socket
object is connected. It returns 0 if the socket is not
connected.
int getLocalPor t( )
Returns the local por t to which the invoking Socket
object is bound. It returns 1 if the socket is not bound.
You can gain access to the input and output streams associated with a Socket by use of
the getInputStream( ) and getOuptutStream( ) methods, as shown here. Each can throw an
IOException if the socket has been invalidated by a loss of connection. These streams are
used exactly like the I/O streams described in Chapter 19 to send and receive data.
InputStream getInputStream( )
Returns the InputStream associated with the
throws IOException
invoking socket.
OutputStream getOutputStream( )
Returns the OutputStream associated with the
throws IOException
invoking socket.
Several other methods are available, including connect( ), which allows you to specify a new
connection; isConnected( ), which returns true if the socket is connected to a server; isBound( ),
which returns true if the socket is bound to an address; and isClosed( ), which returns true
if the socket is closed.
The following program provides a simple Socket example. It opens a connection to a
"whois" port (port 43) on the InterNIC server, sends the command-line argument down the
socket, and then prints the data that is returned. InterNIC will try to look up the argument
as a registered Internet domain name, and then send back the IP address and contact
information for that site.
// Demonstrate Sockets.
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
class Whois {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
int c;
// Create a socket connected to internic.net, port 43.
Socket s = new Socket("internic.net", 43);
// Obtain input and output streams.
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
// Construct a request string.
Search WWH :