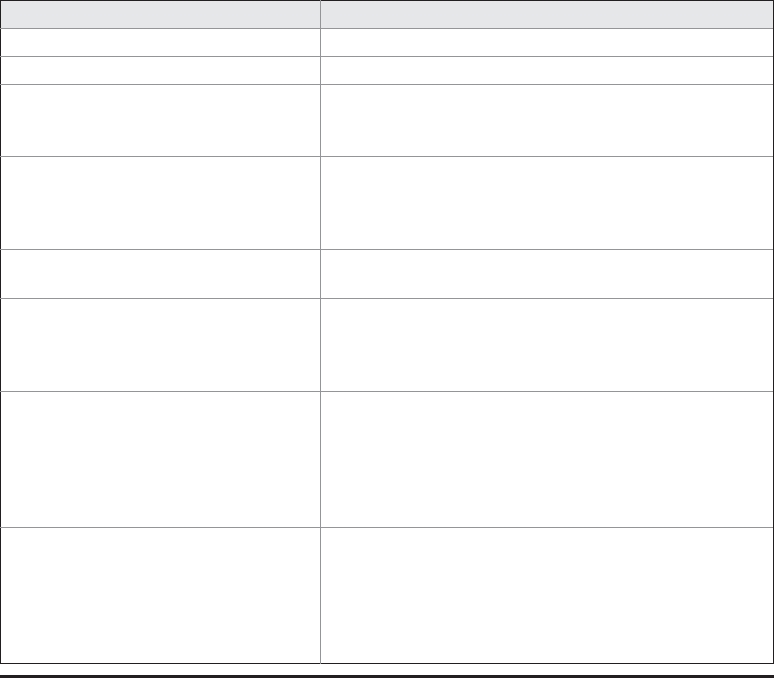
Method
Description
void cancel( )
Cancels the timer thread.
int purge( )
Deletes cancelled tasks from the timer's queue.
void schedule(TimerTask TTask,
TTask is scheduled for execution after the period passed
long wait)
in wait has elapsed. The wait parameter is specified in
milliseconds.
void schedule(TimerTask TTask,
TTask is scheduled for execution after the period passed
long wait, long repeat)
in wait has elapsed. The task is then executed repeatedly
at the inter val specified by repeat. Both wait and repeat
are specified in milliseconds.
void schedule(TimerTask TTask,
TTask is scheduled for execution at the time specified
Date targetTime)
by targetTime.
void schedule(TimerTask TTask,
TTask is scheduled for execution at the time specified
Date targetTime,
by targetTime. The task is then executed repeatedly at
long repeat)
the inter val passed in repeat. The repeat parameter is
specified in milliseconds.
TTask is scheduled for execution after the period passed
void scheduleAtFixedRate(
TimerTask TTask,
in wait has elapsed. The task is then executed repeatedly
long wait, long repeat)
at the inter val specified by repeat. Both wait and repeat
are specified in milliseconds. The time of each repetition is
relative to the first execution, not the preceding execution.
Thus, the overall rate of execution is fixed.
TTask is scheduled for execution at the time specified
void scheduleAtFixedRate(
TimerTask TTask,
by targetTime. The task is then executed repeatedly at
Date targetTime,
the inter val passed in repeat. The repeat parameter is
long repeat)
specified in milliseconds. The time of each repetition is
relative to the first execution, not the preceding execution.
Thus, the overall rate of execution is fixed.
TABLE 18-9
The Methods Defined by Timer
Once a Timer has been created, you will schedule a task by calling schedule( ) on the
Timer that you created. As Table 18-9 shows, there are several forms of schedule( ) which
allow you to schedule tasks in a variety of ways.
If you create a non-daemon task, then you will want to call cancel( ) to end the task when
your program ends. If you don't do this, then your program may "hang" for a period of time.
The following program demonstrates Timer and TimerTask. It defines a timer task whose
run( ) method displays the message "Timer task executed." This task is scheduled to run once
every half second after an initial delay of one second.
// Demonstrate Timer and TimerTask.
import java.util.*;
class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask {
Search WWH :